This post will show you how to control your bicycle fan speed with your heart rate monitor.
DIY KICKR Headwind Parts List
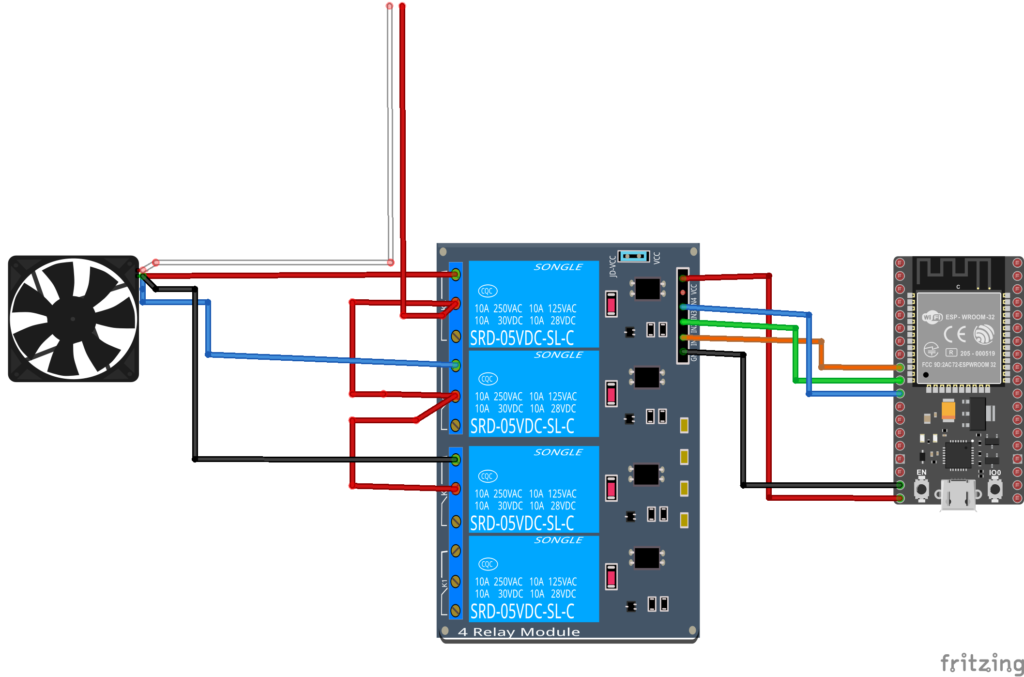
Schematic
DIY KICKR Headwind Code
https://github.com/agrabbs/hrm_fan_control
/**
* A modified BLE client that will read BLE HRM
* and control a relay
* author Andrew Grabbs
*/
#include "BLEDevice.h"
//#include "BLEScan.h"
// Set to true to define Relay as Normally Open (NO)
#define RELAY_NO true
// Set number of relays
#define NUM_RELAYS 3
// Heart Rate Zones
#define ZONE_1 100 // 70 bpm
#define ZONE_2 120 // 100 bpm
// Assign each GPIO to a relay
uint8_t relayGPIOs[NUM_RELAYS] = {25, 26, 27};
// The remote service we wish to connect to.
static BLEUUID serviceUUID("0000180d-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb");
// The characteristic of the remote service we are interested in.
static BLEUUID charUUID(BLEUUID((uint16_t)0x2A37));
//0x2A37
static boolean doConnect = false;
static boolean connected = false;
static boolean notification = false;
static boolean doScan = false;
static BLERemoteCharacteristic* pRemoteCharacteristic;
static BLEAdvertisedDevice* myDevice;
static void notifyCallback(
BLERemoteCharacteristic* pBLERemoteCharacteristic,
uint8_t* pData,
size_t length,
bool isNotify) {
Serial.print("Heart Rate: ");
Serial.print(pData[1], DEC);
Serial.println("bpm");
if(pData[1] == 0) {
for(int i=1; i<=NUM_RELAYS; i++){
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], HIGH);
}
}
else if(pData[1] <= ZONE_1 && pData[1] > 0) {
Serial.println("ZONE 1!");
for(int i=1; i<=NUM_RELAYS; i++){
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[0], LOW);
}
else if(pData[1] > ZONE_1 && pData[1] <= ZONE_2) {
Serial.println("ZONE 2!");
for(int i=1; i<=NUM_RELAYS; i++){
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[1], LOW);
}
else if(pData[1] > ZONE_2) {
Serial.println("ZONE 3!");
for(int i=1; i<=NUM_RELAYS; i++){
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], HIGH);
}
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[2], LOW);
}
}
class MyClientCallback : public BLEClientCallbacks {
void onConnect(BLEClient* pclient) {
}
void onDisconnect(BLEClient* pclient) {
connected = false;
Serial.println("onDisconnect");
}
};
bool connectToServer() {
Serial.print("Forming a connection to ");
Serial.println(myDevice->getAddress().toString().c_str());
BLEClient* pClient = BLEDevice::createClient();
Serial.println(" - Created client");
pClient->setClientCallbacks(new MyClientCallback());
// Connect to the remove BLE Server.
pClient->connect(myDevice); // if you pass BLEAdvertisedDevice instead of address, it will be recognized type of peer device address (public or private)
Serial.println(" - Connected to server");
// Obtain a reference to the service we are after in the remote BLE server.
BLERemoteService* pRemoteService = pClient->getService(serviceUUID);
if (pRemoteService == nullptr) {
Serial.print("Failed to find our service UUID: ");
Serial.println(serviceUUID.toString().c_str());
pClient->disconnect();
return false;
}
Serial.println(" - Found our service");
// Obtain a reference to the characteristic in the service of the remote BLE server.
pRemoteCharacteristic = pRemoteService->getCharacteristic(charUUID);
if (pRemoteCharacteristic == nullptr) {
Serial.print("Failed to find our characteristic UUID: ");
Serial.println(charUUID.toString().c_str());
pClient->disconnect();
return false;
}
Serial.println(" - Found our characteristic");
// Read the value of the characteristic.
if(pRemoteCharacteristic->canRead()) {
std::string value = pRemoteCharacteristic->readValue();
Serial.print("The characteristic value was: ");
Serial.println(value.c_str());
}
if(pRemoteCharacteristic->canNotify())
pRemoteCharacteristic->registerForNotify(notifyCallback);
connected = true;
return true;
}
/**
* Scan for BLE servers and find the first one that advertises the service we are looking for.
*/
class MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks: public BLEAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks {
/**
* Called for each advertising BLE server.
*/
void onResult(BLEAdvertisedDevice advertisedDevice) {
Serial.print("BLE Advertised Device found: ");
Serial.println(advertisedDevice.toString().c_str());
// We have found a device, let us now see if it contains the service we are looking for.
if (advertisedDevice.haveServiceUUID() && advertisedDevice.isAdvertisingService(serviceUUID)) {
BLEDevice::getScan()->stop();
myDevice = new BLEAdvertisedDevice(advertisedDevice);
doConnect = true;
doScan = true;
} // Found our server
} // onResult
}; // MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println("Starting Arduino BLE Client application...");
BLEDevice::init("");
// Set all relays to off when the program starts - if set to Normally Open (NO), the relay is off when you set the relay to HIGH
for(int i=1; i<=NUM_RELAYS; i++){
pinMode(relayGPIOs[i-1], OUTPUT);
if(RELAY_NO){
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], HIGH);
}
else{
digitalWrite(relayGPIOs[i-1], LOW);
}
}
// Retrieve a Scanner and set the callback we want to use to be informed when we
// have detected a new device. Specify that we want active scanning and start the
// scan to run for 5 seconds.
BLEScan* pBLEScan = BLEDevice::getScan();
pBLEScan->setAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks(new MyAdvertisedDeviceCallbacks());
pBLEScan->setInterval(1349);
pBLEScan->setWindow(449);
pBLEScan->setActiveScan(true);
pBLEScan->start(5, false);
} // End of setup.
// This is the Arduino main loop function.
void loop() {
// If the flag "doConnect" is true then we have scanned for and found the desired
// BLE Server with which we wish to connect. Now we connect to it. Once we are
// connected we set the connected flag to be true.
if (doConnect == true) {
if (connectToServer()) {
Serial.println("We are now connected to the BLE Server.");
} else {
Serial.println("We have failed to connect to the server; there is nothin more we will do.");
}
doConnect = false;
}
// If we are connected to a peer BLE Server, update the characteristic each time we are reached
// with the current time since boot.
if (connected) {
if (notification == false) {
Serial.println("Turning Notification On");
const uint8_t onPacket[] = {0x01, 0x0};
pRemoteCharacteristic->getDescriptor(BLEUUID((uint16_t)0x2902))->writeValue((uint8_t*)onPacket, 2, true);
notification = true;
}
}else if(doScan){
BLEDevice::getScan()->start(0); // this is just eample to start scan after disconnect, most likely there is better way to do it in arduino
}
delay(1000); // Delay a second between loops.
} // End of loop

Awesome writeup and video. Managed to replicate this with my own FAN and it worked ! Am thinking about some modifications (Wifi connected for easier updates/mods and a temperature sensor)
Thanks! Those modifications sound pretty cool, let me know what you settle on.
Pretty cool, I was just thinking about doing something like this.
I think my approach would be to get a 5-6-7-8 speed fan with an IR remote and use an IR blaster or Broadlink device to control it based on speed or heart rate. I’ll definitely use your work as a reference, thanks!
Thank you for posting this!
I’m not much of a coder, but if I want to use my trainer’s speed (like the Kickr Headwind) to control the fan rather than an HRM, how would I go about doing this?
Hi Andrew,
Hi everyone,
I have seen you project and it looks really great. I have got a Honeywell TurboForce with 3 speed. Do you think this will work with it?
Thanks a lot.
Best regards.
Martin
Should be good!
Thanks so much for the tutorial. I bought a Lasco high velocity fan and did this. I also added a 16×2 LCD that displays what zone the fan is in and current heart rate! The only thing that is a little funky is the initial connection. Thanks again.
Dario,
It looks like you are doing `if(pData[1] == 99) {` That line states if the data is 99. So your code suggest that only if the data is 99 do you set all relays HIGH. I would do something along the lines of `if pdata >= 99 { set to high if not already on high }`. Hope that helps!
Thank you. Works great. Regards